What is the Difference between a Tumor and Cancer?
Many individuals consider the terms tumor and cancer to be compatible; however, they are not. Although tumors can be cancerous, not every one of them are. Also, not all cancer cells create tumors. For instance leukemia (blood cancer), kinds of lymphoma, and myeloma.
A tumor, in Latin, merely implies “swelling”. A tumor is a mass of unusual cells or cells in the body. Occasionally they are also called “swelling”, “mass”, “sore”, “growth”, or “neoplasm”. When cells divide quicker than typical or fail to pass away when they should, a tumor establishes. Growths can be either benign or malignant.
Benign tumors are noncancerous; they do not invade (eat away right into regular tissues) or infected other parts of the body. To understand a lot more, book a consultation at our cancer treatment healthcare facility in Millers Road, Bangalore.
Malignant tumors are cancerous. They can attack into surrounding cells, or spread to other parts of the body and ultimately come to be fatal. There are more than 100 types of cancer cells which are typically named for the organs or cells where the cancer cells create, for example, breast cancer cells, colon cancer, lung cancer, or skin cancer. Cancer can additionally be defined by the type of cell that ended up being malignant. As an example, adenocarcinoma forms in cells that comprise glands. A sarcoma is in bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, capillary, or various other connective or helpful tissues.
When cancer cells different from a malignant tumor and go into the lymphatic or blood systems, the procedure is called metastasis. When cancer cells metastasize, they can settle in other body organs. The location where the cancer cells’ very first type is called the main site. Metastasis to a brand-new location is called a second website.
Understanding Tumor
Growths can be split right into two major classifications: Benign and Deadly. Benign Tumors are noncancerous and do not spread to other parts of the body. Malignant Growths, on the other hand, are malignant and can infect other parts of the body if left unattended. Precancerous Tumors are uncommon developments in the body that have the prospective to become cancer cells. These tumors can be discovered in different parts of the body, such as the skin, cervix, lungs, and other organs. It is necessary to recognize precancerous lumps early on so that they can be dealt with before they become cancerous.
There are additionally a variety of various other sorts of growths, such as lymphomas, sarcomas, bacterial cell growths, and extra. Each sort of tumor has the unique qualities that make it different from the others. Understanding these distinctions is important to precisely detect and treat them.
Understanding Cancer
It is a group of conditions that can influence any kind of part of the body and can be triggered by many different variables. Cancer occurs when cells in the body grow abnormally and split frantically, creating growths or infecting various other parts of the body. Some typical types of cancer cells consist of lung cancer cells, colon cancer, breast cancer cells, skin cancer, prostate cancer, and blood cancer cells. Each kind of cancer cell has its very own special set of signs and treatments.
Early detection and therapy are essential to successfully managing cancer cells, so it is very important to comprehend what it is and how it works. Let’s understand these terms in detail.
What is Tumor?
A tumor refers to irregular mobile growth. Benign growths are non-cancerous, commonly localized, and generally have a marginal threat to wellness unless they exert stress on important structures. Malignant growths are characterized by unchecked mobile growth and department, right into bordering cells, and metastasis to far-off organs. Reasons vary from genetic anomalies to environmental elements like tobacco and UV exposure. The diagnosis of a lump is made with the help of imaging scans, biopsies, and molecular tests. Therapy treatments vary and include surgical treatment, radiation treatment, radiation treatment, immunotherapy, and targeted treatment.
What are the Different Types of Tumors?
Understanding the different kinds of growths is essential for accurate diagnosis, diagnosis, and therapy preparation. From benign developments to malignant growths that are capable of metastasis, each lump kind presents obstacles to the medical professionals. Several of the kinds of lumps are:
Malignant
Malignant growths are normally referred to as cancer cells. These tumors, or cancerous swellings, are characterized by unrestrained cell growth, intrusive habits, and the prospective to infect distant body organs. These aggressive lumps trigger substantial health threats, interfere with typical cell function, and may cause incapacitating symptoms. They might occur because of hereditary mutations or environmental elements. Deadly tumors evade the immune system, divide and expand uncontrollably, and interrupt the surrounding tissues, bringing about signs of cancer.
Non-Malignant
Non-malignant or non-cancerous lumps are benign growths or abnormal cell masses that do not get into close-by tissues or technique to distant body organs. While people might have non-malignant growth symptoms relying on their size and place, they normally have relatively fewer health complications than deadly tumors. These growths generally have sluggish development rates and may stay asymptomatic for long term periods.
Precancerous
Precancerous tumors are additionally known as pre-neoplastic lesions. They stand for irregular cell growth with the prospective to develop into cancer if left without treatment. These lesions have atypical mobile modifications, suggesting a progression towards malignancy. Discovery and surveillance of precancerous growths support very early intervention and play a crucial function in stopping the development of invasive cancer.
What is Cancer?
Cancer happens when the cells grow frantically, form masses, and spread to neighboring and far-off organs. It can affect tissue or body organs, interfere with regular bodily functions, and cause extreme wellness difficulties. Causes consist of genetic tendencies, ecological factors like tobacco and ultraviolet radiation, and lifestyle selections. Commonly utilized cancer medical diagnosis strategies to identify cancer cells types and phases consist of imaging, biopsies, and molecular tests. Therapies include surgical procedure, chemotherapy, radiation treatment, immunotherapy, and targeted treatment.
Types of Cancer
Cancer is identified by the uncommon development of cells in various body components, each with one-of-a-kind characteristics. Recognizing the differences in these features is essential for precise medical diagnosis and personalized therapy methods. Several of the kinds of cancer cells are:
Carcinoma
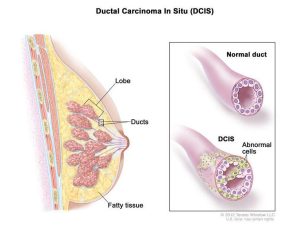
Carcinoma is one of the most common types of cancer. It launches in the epithelial tissues lining body organs and body surfaces. They include squamous cell carcinomas (skin, lungs, and esophagus), adenocarcinomas (glandular cells), and basic cell carcinomas (skin). Early detection with screening techniques like mammograms and Pap smears improves treatment results.
Sarcoma
These cancers cells create in connective cells, such as bones, muscle mass, fat, and blood vessels. They are relatively less common compared to cancers. Types include liposarcoma (fat), osteosarcoma (bone), and leiomyosarcoma (smooth muscle).
Leukemia
It is a cancer of the blood-forming tissues, consisting of the bone marrow and lymphatic system. The illness is defined by the abnormal manufacturing of white blood cells. Kinds consist of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), severe myeloid leukemia (AML), and persistent myeloid leukemia (CML).
Lymphoma
These are cancers originating in the lymphatic system. They consist of Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), with NHL being extra common. Treatment consists of chemotherapy, radiation treatment, immunotherapy, and stem cell transplant.
Melanoma
It is a type of skin cancer originating in melanocytes. Melanocytes are the cells that produce melanin. It can be created on normal skin or from existing moles. Cancer malignancy is very hostile and susceptible to transition if not discovered early.
Leading 4 Differences Between Tumor and Cancer cells
Tumor and cancer cells are often used interchangeably, but they have distinctive significance in clinical terms. It is necessary to comprehend the distinctions between lumps and cancer. The adhering to are the crucial aspects of growth vs cancer cells:
Cancer cells are a condition … Tumor can be
Cancer cells are a malignant illness that can infect numerous parts of the body and cause numerous health complications. Tumors, on the other hand, describe uncommon developments, which might be benign or malignant. While all cancers are growths, not all growths are cancerous; some may be benign and position very little health and wellness risks.
Cancer is comprised of deadly cells, while Tumor are not constantly
Cancer includes malignant cells that multiply uncontrollably, forming invasive growths capable of transition. On the other hand, tumors can be benign or deadly; benign tumors can not spread out.
Cancer can be lethal, tumors do not need to be
Cancer, with its ability to spread to nearby and distant body organs, can be deadly, usually causing extreme wellness problems, consisting of death, if neglected. In contrast, benign tumors may trigger wellness issues that might not necessarily be life-threatening.
Cancer can cause transition, Tumor don’t constantly
Cancer cells have the prospective to technique and considerably impact the prognosis. On the other hand, growth is not always a technique. While malignant tumors can spread, benign growths typically continue to be local and do not attack close-by cells or metastasize.
Not all tumors are cancerous
It is necessary to comprehend that not all lumps are malignant. There are benign lumps where the development is limited to certain parts of the body. A growth comes to be cancer when it is deadly. This suggests that the key development can generate several secondary growths therefore getting into vital parts of your body and spreading anywhere.
Just as all growths are not malignant, all cancer cases are additionally not identified by lump development. As an example, in case of blood cancer, there is no lump included. However, on looking at a lump, biopsy ends up being really vital to determine if its growth is malignant or benign.
A tumor might or might not turn into cancer. Cancer on the other hand is a deadly problem in which the spread of abnormal mobile growth can end up being unmanageable.
What are the Causes or Sources of Cancer?
The root causes of cancer cells include an interplay of genetic, environmental, and way of life variables. Hereditary anomalies gotten during life or inherited from moms and dads can interfere with regular cell growth guidelines, leading to cancer. Environmental exposures such as cigarette smoke, ultraviolet radiation, and carcinogenic chemicals may additionally lead to DNA damage and consequently increase cancer threat.
Lifestyle choices like absence of physical activity, bad diet regimen, and too much alcohol consumption likewise contribute to creating cancer. Chronic infections from infections like HPV and liver disease B and C can incline individuals to certain cancers cells. Comprehending and reducing these risk variables with safety nets, screening, and early discovery are important.
How Does Cancer Develop?
Cancer is caused by specific modifications to genes, the basic physical systems of inheritance. Genetics are organized in lengthy strands of snugly packed DNA called chromosomes.
Hereditary adjustments that cause cancer can take place due to the fact that:
- of errors that happen as cells divide.
- of damages to DNA brought on by unsafe materials in the environment, such as the chemicals in cigarette smoke and ultraviolet rays from the sun. (Our Cancer Cells Causes and Avoidance section has more details.).
- they were inherited from our parents.
The body normally gets rid of cells with damaged DNA prior to they transform cancerous. However the body’s ability to do so goes down as we age. This becomes part of the reason why there is a greater threat of cancer cells later on in life.
Each person’s cancer has a distinct mix of genetic adjustments. As the cancer continues to grow, extra modifications will take place. Also within the exact same tumor, different cells might have various hereditary changes.
Types of Genes that Create Cancer Cells
The genetic adjustments that add to cancer often tend to influence 3 main sorts of genes– proto-oncogenes, tumor suppressor genetics, and DNA repair genetics. These modifications are often called “chauffeurs” of cancer cells.
Proto-oncogenes are associated with typical cell growth and division. Nevertheless, when these genes are altered in certain ways or are extra active than typical, they may end up being cancer-causing genes (or oncogenes), enabling cells to expand and endure when they ought to not.
Tumor suppressor genes are likewise associated with regulating cell growth and division. Cells with certain alterations in tumor suppressor genetics may split in an uncontrolled way.
DNA repair service genes are associated with dealing with damaged DNA. Cells with mutations in these genes have a tendency to create added mutations in other genes and adjustments in their chromosomes, such as duplications and removals of chromosome components. Together, these mutations might create the cells to become cancerous.
As scientists have actually learned more about the molecular adjustments that result in cancer cells, they have actually discovered that certain mutations commonly take place in several sorts of cancer cells. Now there are many cancer treatments offered that target genetic mutations discovered in cancer. A few of these treatments can be made use of by anyone with cancer cells that has actually the targeted mutation, regardless of where the cancer began growing.
When Cancer Spreads
A cancer that has spread from the area where it first created to one more place in the body is called metastatic cancer cells. The process through which cancer cells infect various other parts of the body is called metastasis.
Metastatic cancer cells have the very same name and the very same sort of cancer cells as the initial, or primary, cancer cells. For example, breast cancer that develops a metastatic tumor in the lung is metastatic breast cancer cells, not lung cancer cells.
Under a microscope, metastatic cancer cells typically look like the cells of the initial cancer cells. Furthermore, metastatic cancer cells and cells of the original cancer normally have some molecular attributes alike, such as the existence of detailed chromosome modifications.
In many cases, treatment might aid prolong the lives of people with metastatic cancer. In various other instances, the key goal of therapy for metastatic cancer is to control the growth of the cancer cells or to alleviate symptoms it is creating. Metastatic lumps can create extreme damages to exactly how the body features, and lots of people that pass away of cancer cells die of metastatic disease.
Treatment of Tumor and Cancer Cells
Malignant or benign tumors can be determined by a simple health examination through palpation or with imaging strategies such as X-ray and MRI scans, and tests such as biopsy, and so on. All of these procedures help to recognize the size and shape of the lump, its location in the body, and any other linked signs and symptoms that may show hatred.
With these exams, being the best cancer hospital in India, our oncologists can diagnose cancer cells precisely and quickly so that suitable treatment can be carried out asap. We hope you locate this blog informative. Get the word out and feel free to contact us for cancer cells treatment at Denvax India.
Also Read: Best Lung Cancer Treatment in India